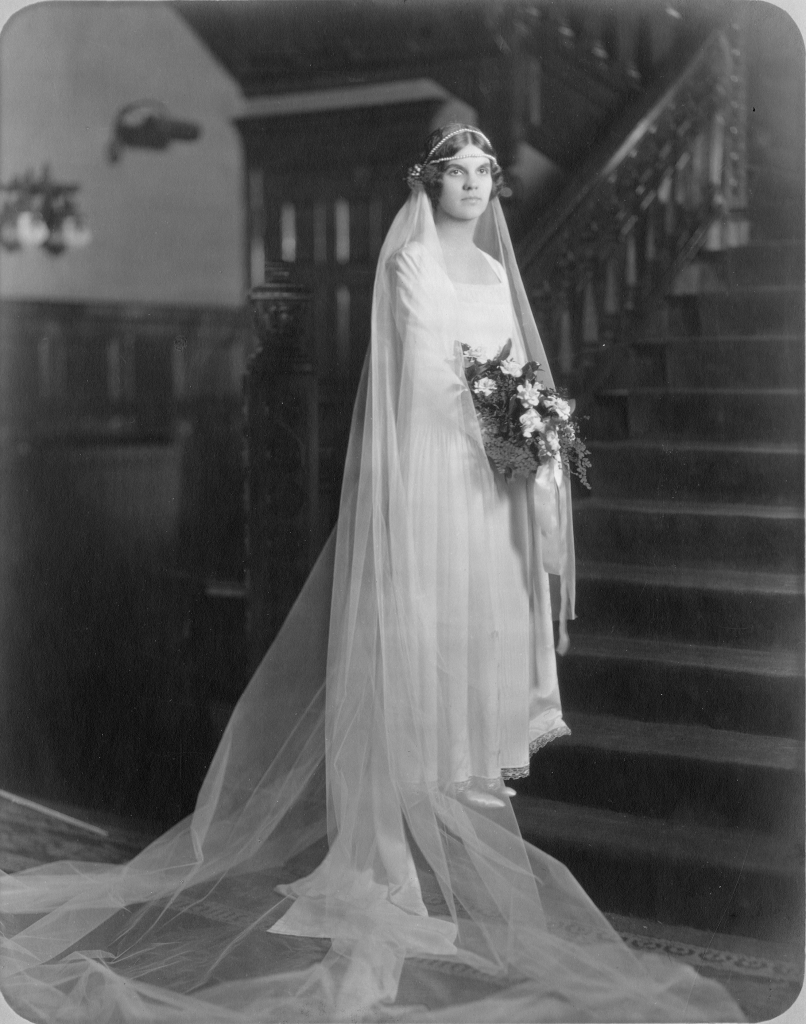
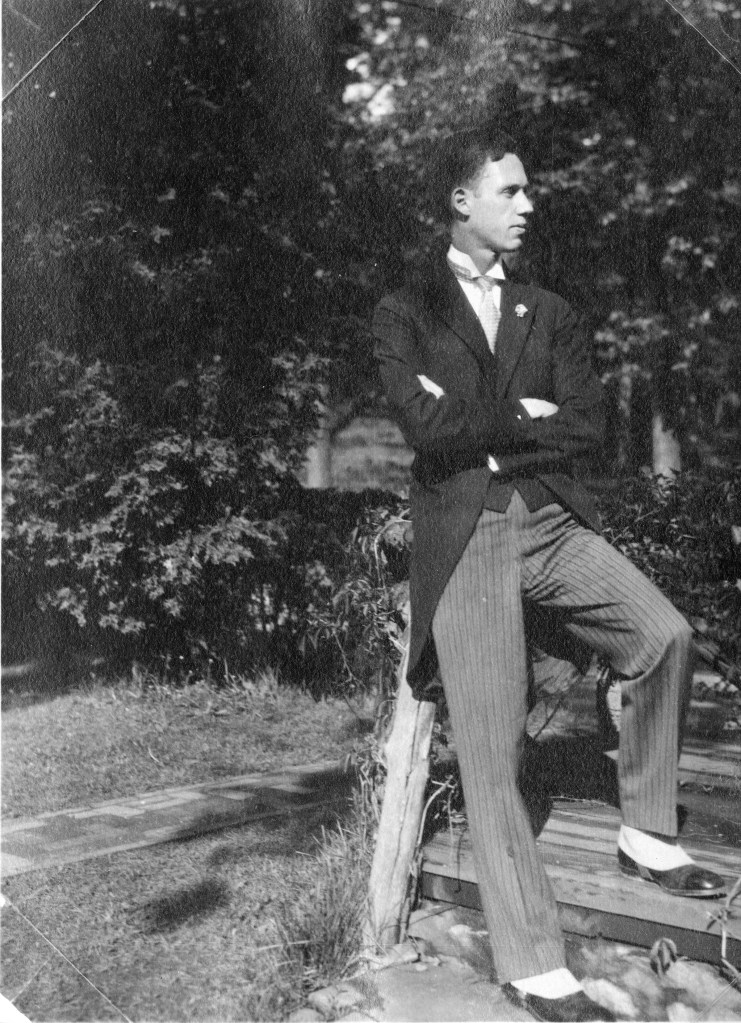
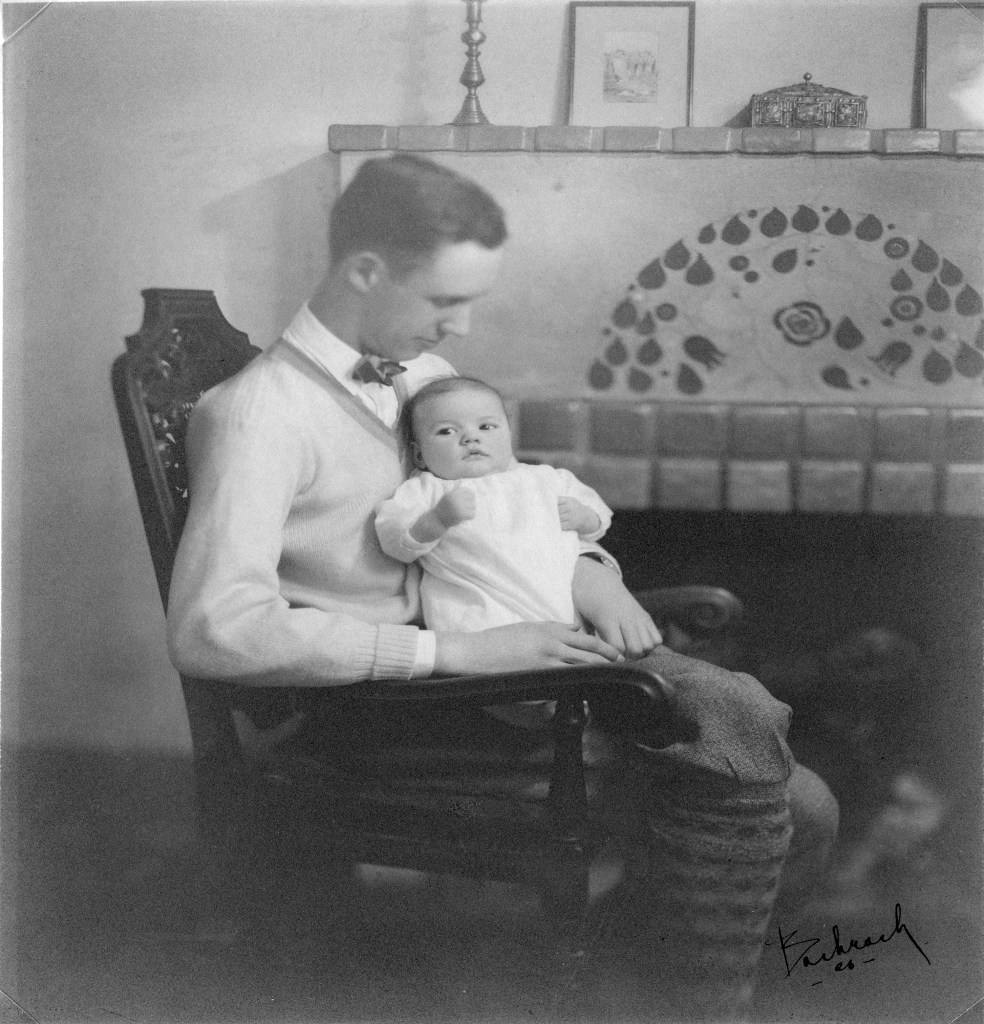
With thousands of years of recorded history to draw from, every day of the year has some distinction as an anniversary. Today, the 27th of September, is the 958th anniversary of the day William, Duke of Normandy, set sail to conquer England, the 560th anniversary of the birth of Cosimo de’ Medici, founder of the de facto ruling family of Renaissance Florence, and the 100th anniversary of the wedding of Henry Scripps Booth to Carolyn Elizabeth Farr. Here at Cranbrook, it is this last anniversary that holds top billing on our calendars.
Henry Booth, youngest son of Cranbrook’s founders, George and Ellen Booth, and Carolyn Farr, daughter of shipbuilding magnate Merton Elmer Farr and Emma Rothe, first announced their engagement on June 29th, 1925. Neither of them believed in long engagements, it appears, as they were married just three months later, at the First Congregational Church in Detroit. The wedding had some competition for most memorable event of the year for Carolyn Farr. On August 30th, while on her way home from a shopping trip to New York City to complete her trousseau, Carolyn’s train crashed into the back of another train which had made an accidental stop on the westbound line near Syracuse.
Fortunately, no one was killed in the crash. Some members of a Boy Scouts troop riding at the back of the rear train actually slept through the collision and had to be shaken awake by their bemused troop leaders. Though she escaped serious injury, the crash left Carolyn with cuts on her nose and mouth, which may have still been painful on her wedding day, though they are invisible in her wedding photos.
Both of Henry’s sisters were married at Cranbrook House itself, Grace Booth in the living room and Florence Booth in the library. Although Henry was not married at Cranbrook, the wedding was still very much a Cranbrook event in one way, because it featured an Arts and Crafts artwork. The ring was carried down the aisle by Carolyn’s nephew, Henry Gerhauser, in a silver and enamel box made by the noted Boston-based artist Elizabeth Copeland.
Enameling, like tapestry weaving and illumination, was a medieval art form revived by the Arts and Crafts movement in England in the nineteenth century. In the twentieth century, enameling evolved out of the medievalist styles that characterized its revival to become a primary medium of both Art Nouveau and Art Deco decorative art and jewelry.
Elizabeth Copeland was the foremost enamel artist of the American Arts and Crafts movement. Born in Revere, Massachusetts in 1866, she did not begin her artistic training until she was in her early thirties. Like many women artists, she was expected to balance her own work with domestic labor. Copeland had to commute daily to attend the Cowles Art School in Boston, and she studied her design patterns while carrying out household chores. So great was her talent, however, that within just a few years her enamels and silver work were already enjoying critical acclaim, including a feature in Craftsman magazine in 1903. Her work is now in many museum collections, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the Art Institute of Chicago, and the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
As an artist, Copeland embraced the Arts and Crafts movement’s ideals. Eschewing a machine-like precision in her work, her silver work proudly exhibits subtle variations and inconsistencies that distinguish them as truly hand-crafted objects. Her enamel work embraces the fluidity of the medium, allowing different colors to flow into one another within each metal embrasure shaped to contain the liquid medium. Unlike most women artists of her time, Copeland was able to support herself independently through the sale of her work, during a career of more than three decades. She exhibited her work at many venues, including the Detroit Society of Arts and Crafts, where Henry Scripps Booth purchased the silver box that would hold the ring for his wedding, two years later.
After the wedding, the new couple moved into Brookside Cottage, the little stone house just west of Kingswood School, where they lived for two years until Thornlea House was completed. The Copeland box became a fixture of their new home, where they lived together from 1927 until Carolyn’s death in 1984. During her lifetime, the ring box spent many years on a table in Carolyn’s own bedroom, as a memento of a milestone occasion which we are celebrating again, one hundred years down the line.
— Mariam Hale, 2023-2025 Collections Fellow, Cranbrook Center for Collections and Research