Did you ever watch the show History Detectives on PBS? I loved the show; it is all about uncovering the story of an object.
As Associate Registrar for the Center, I am working with our Director Gregory Wittkopp and our Associate Curator Kevin Adkisson on an ambitious project. We are reviewing all fourteen of our cultural properties collections (over 9,000 objects), reviewing the data already on file and adding as much additional information about each object as we can. How do we do this, when the people who created, collected, or purchased the objects are no longer here? It requires being something of a history detective!
The collection we are currently working on is the Cultural Properties Collection at Thornlea. Thornlea was the home of George and Ellen Booth’s youngest son, Henry Scripps Booth, and his wife, Carolyn Farr Booth, from 1926 to 1988. It is filled with antiques, artwork, furnishings, and personal objects. In Cranbrook Archives, there are multiple helpful records about the home’s collections: insurance inventories, an index card file of objects created and maintained by Henry, and receipts for items purchased.
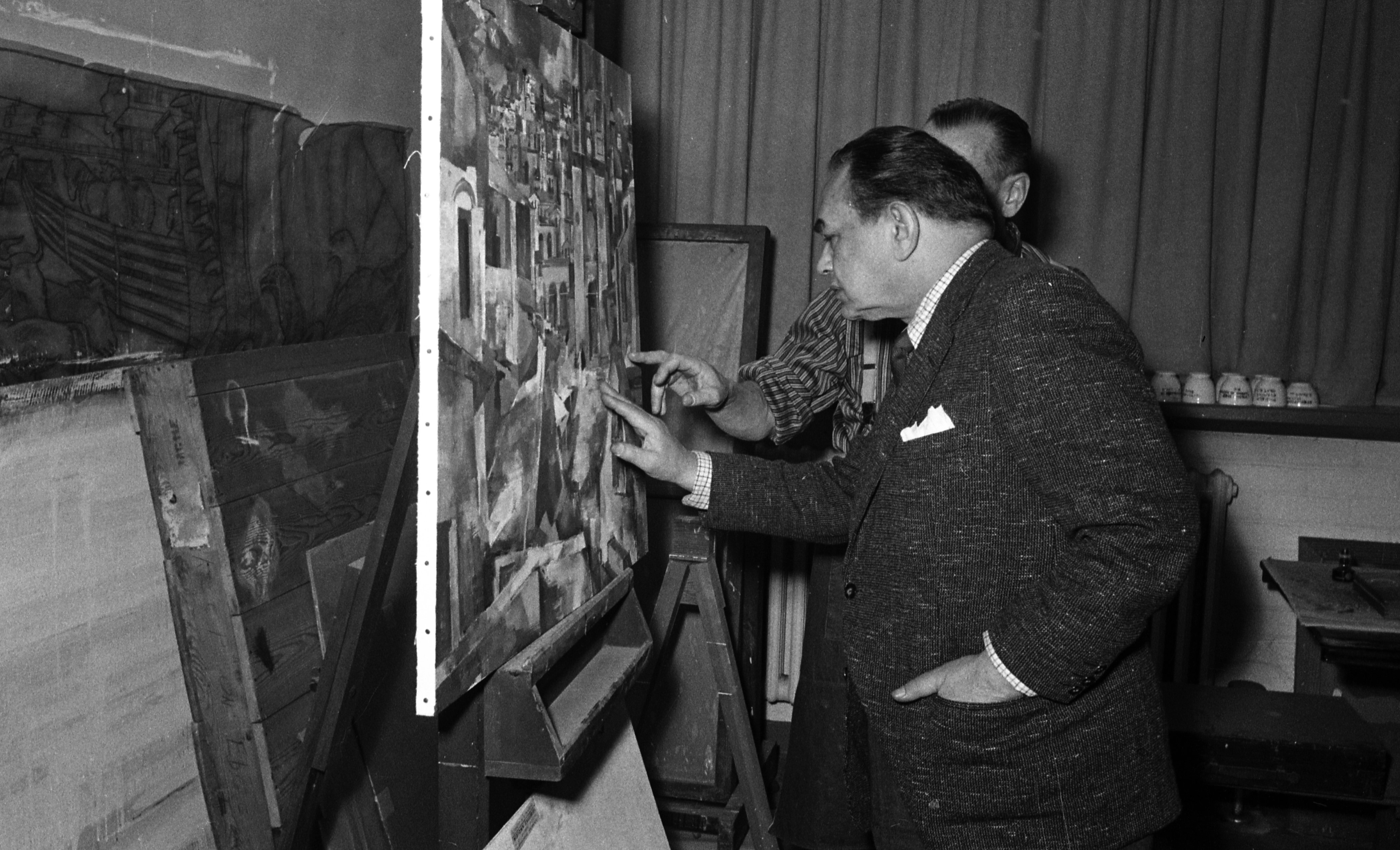
The one object I wanted to feature today is the unique light fixture over the front door to Thornlea. This custom and distinctive iron and glass fixture is important to the architectural character of the house, but I knew next to nothing about it. It appeared in early images of the house, so I knew it had been a part of the house from the earliest years, perhaps since the house was built.
To learn more about the fixture, I first looked at the insurance inventories and Henry’s index card file. Nothing there.
Next, I looked at the receipts under “Electrical” in the Henry Scripps and Carolyn Farr Booth Papers in Archives. Eureka!
Continue reading